Q.
Differentiate the following. Support your answer with examples.
i) Government Operating Expenditure and Government Development Expenditure. (10 marks)
ii) Tariffs and Quota as a tool of protectionism. (10 marks)
(20 marks, 2012 Q8)
A.
ii)
Tariffs
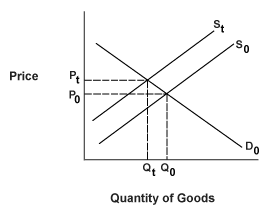
Tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods; they will increase the price of the good in the domestic market. Domestic producers benefit because they receive higher prices. The government benefits by collecting tax revenues. In the graph below, S0 and D0 represent the original supply and demand curves which intersect at (P0, Q0). St shows what the supply curve is with the introduction of the tariff. The market then clears at (Pt, Qt). Less of the good is produced, and consumers pay higher prices.
Figure 5.5: Effect of a Tariff on a Supply Curve
 |
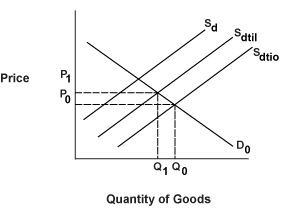
Quotas are numerical limits imposed on imported goods. Consumers are harmed by quotas, while domestic and foreign producers benefit by receiving higher prices. In the graph below, the market initially clears at P0, Q0. The supply curve Sd+i0represents the quantity supplied by both domestic and foreign producers before the imposition of the quota. D0 is the domestic demand curve. After the quota, the supply curve looks like Sd+i1. Both foreign and domestic producers receive higher prices while consumers lose out.
Figure 5.6: Effect of Quotas on the Supply Curve
 |
[Both tariff and quota are means of protectionism because it fences out competition. In the context of tariff, the taxes on imported goods increase the price of goods produced by competitors abroad, therefore protecting the local producers. In the context of quota, the limited imports restrict availability of the competitor goods, thus allowing the local producers to fulfill the demand which is unmet.
Example on tariff, the government protects the national car industry by imposing tariff on foreign cars so as to rise car prices locally to enable national car to sell at higher than international price. Thus, it creates a barrier to competition by raising the cost of selling foreign car in the country.
Example on quota, the government protects the local employment market by imposing quota on foreign workers. As there are limited foreign workers, the wage rises for locals as local workers would not take up jobs that pay less than their expectation. It thus protects the locals from being underpaid by employers.]
Ref:
http://www.investopedia.com/exam-guide/cfa-level-1/global-economic-analysis/tariffs-quotas.asp
[x] are based on own account.