Q.
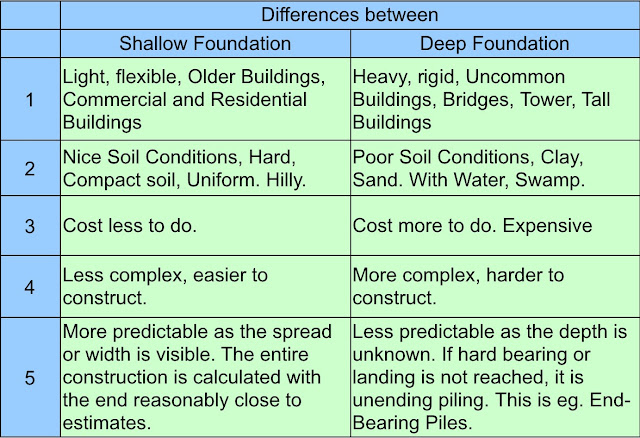
a) List five (5) differences between shallow and deep foundation. (10 marks)
b) Sheet pile walls are constructed by driving prefabricated sections into the ground. With the aid of sketches, explain the method of installing sheet pile. (15 marks)
(25 marks, 2014 Q2)
A.
Shallow foundation:
A type of foundation that is used when the earth directly beneath a structure has sufficient bearing capacity to sustain the loads from the structure .
The characteristics of the deep foundations are as follow.
A type of foundation that is used when the soil near the ground surface is weak.
Properties of steel sheet-pile walls
Sheet-pile walls are made from linked sheet piles that are long steel plates with a Z or U shape. These piles are connected together to make a sealed wall. Sheet piles are often connected together in pairs and installed using one of three methods:
- Vibration: this is the most common method. The first sheet pile of the wall is installed into the ground. A vibratory hammer with clamp is attached to the top of the second sheet pile, which is then interlocked with the first sheet pile, and the sheet pile is vibrated into the ground.
- Pressing: sheet piles can also be pressed into the ground when noise hindrance and vibration would otherwise cause problems. This, however, takes longer and is expensive. The sheet piles are pressed into the ground by a hydraulic machine.
- Excavation: sheet piles can also be excavated into the soil. A long trench is excavated which is then filled with cement bentonite (a thin concrete slurry) to prevent the walls from collapsing. The sheet piles are then installed in the trench and the cement bentonite is allowed to set.
Steel sheet-pile walls can retain both soil and water. The retaining height of the sheet-pile wall can be increased by driving anchors or MV piles into the ground. This increases the strength of the structure: the anchors prevent the sheet-pile wall from being forced inwards by the force of the soil or water.
Use of sheet-pile walls
Sheet-pile walls are used for both temporary and permanent purposes. They are, for example, suitable for creating a sufficiently deep workplace in the form of an excavation pit below ground level; they retain the soil or water to enable the construction. Sheet-pile walls are used in permanent structures such as quay walls or tunnel walls.
Ref:
Steel Sheet Pile Wall, available at
http://www.bnft.nl/page_2526.asp