Q.
(a) With the use of diagrams, explain the methods of supporting the ends of joists and the types of joist strutting in the construction of the timber upper floor. (15 marks)
(b) Explain the suitable materials used for damp proof membrane in ground floor construction. (10 marks)
(25 marks, 2016 Q3)
A.
a) Timber upper floor is a common question:
Using diagram, explain timber upper floor
However, this question asked about methods of supporting the ends of joists and the types of joist strutting, not about drawing of timber upper floor.
First, the joist - which are long timber beams, forming skeleton frame for the entire support of the flooring on top. The end of joists must be anchored into the wall which hold these joists up.
Timber joists used for upper floors are supported at ends by either the external wall or by internal loadbearing partition walls. As with ground floors, the joist section size will be determined by the span length and the floor loading.
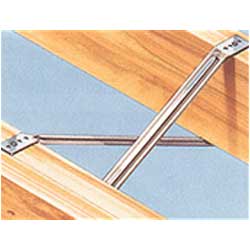
The joists used may be of solid timber, be constructed of composite plywood I-beams or composite metal web beams. How it sits into the wall and other loadbearing timber beams is what is asked about in this question.
Then, the completed diagram would look like below.
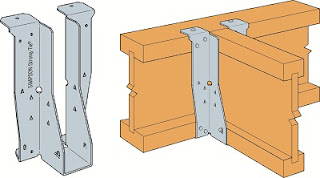
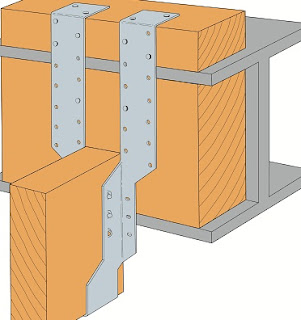
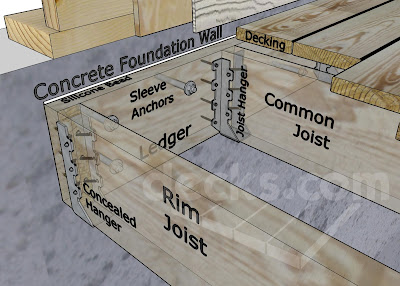
2. If it does not sit inside the wall it can be secured onto the wall with hanger devices like below:
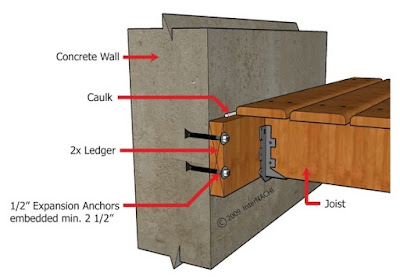
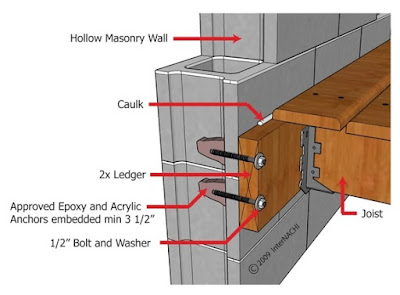
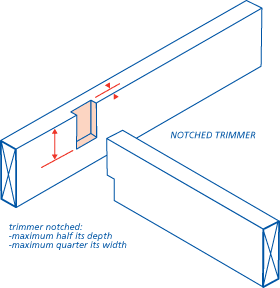
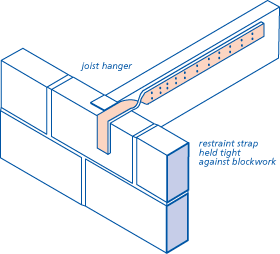
A long beam of solid timber is fastened into the wall by using screws (wall bolts) like above, and the joist timber beams sits on this fastened timber beam. It can be secured by i-joist hanger or notched trimmer like below.
The completed timber upper floor will look like the diagram below.
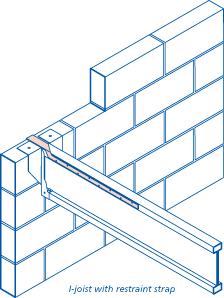
In this diagram the joists is embedded into the wall.
Below diagram is timber upper floor joists secured by beam fastened onto concrete wall by wall bolts.
Ref:
Various images from google search.
b) Damp Proof Membrance Pictures:
Ref:
Various images from google search "damp proof membrane"