Q.
a) Describe the functions of building foundation. (10 marks)
b) Using diagrams, explain the following types of foundation. State the type of soil and the type of building structure where the foundation should be used.
i. Wide strip foundation (5 marks)
ii. Pad foundation (5 marks)
iii. Raft foundation (5 marks)
(25 marks, 2017 Q2)
A.
a) Functions of building foundation
FUNCTIONS OF FOUNDATION
1. REDUCTION OF LOAD INTENSITY
Foundation distributes the loads of the super structure, to a larger area so that the intensity of the load at its base (i.e. total load divided by the total area) does not exceed the safe bearing capacity of the sub-soil.
2. EVEN DISTRIBUTION OF LOAD
Foundations distribute the non-uniform load of the super structure evenly to the sub soil. For example, two columns carrying unequal loads can have a combined footing which may transmit the load to sub soil evenly with uniform soil pressure. Due to this, unequal or differential settlements are minimized.
3. PROVISION OF LEVEL SURFACE
Foundation provide leveled and hard surface over which the super structure can be built.
4. LATERAL STABILITY
It anchors the super structure to the ground, thus imparting lateral stability to the super structure. The stability of the building, against sliding and overturning, due to horizontal forces (such as wind, earthquake etc.) is increased due to foundations.
5. SAFETY AGAINST UNDERMINING
It provides the structural safety against undermining or scouring due to burrowing animals and flood water.
6. PROTECTION AGAINST SOIL MOVEMENTS
Special foundation measures prevents or minimizes the distress (or cracks) in the super structure, due to expansion or contraction of the sub soil because of moisture movement in some problematic soils.
Ref:
http://civilblog.org/2015/01/26/what-are-the-functions-of-foundation/
b) Type of soil and the type of building structure
Similar question was asked in
2016 Q2
Varied soil and various foundation type (*IMPORTANT READ*)
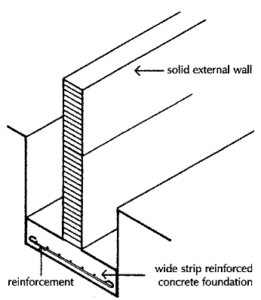
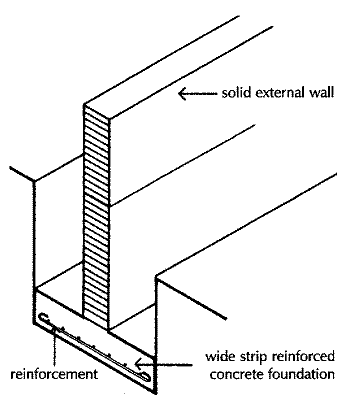
i. Wide strip foundation
Strip foundations consist of a continuous strip, usually of concrete, formed centrally under load bearing walls. This continuous strip serves as a level base on which the wall is built and is of such a width as is necessary to spread the load on the foundations to an area of subsoil capable of supporting the load without undue compaction. Concrete is the material principally used today for foundations as it can readily be placed, spread and levelled in foundation trenches, to provide a base for walls, and it develops adequate compressive strength as it hardens to support the load on foundations. Before Portland cement was manufactured, strip foundations of brick were common, the brick foundation being built directly off firm subsoil or built on a bed of natural stones.
The width of a concrete strip foundation depends on the bearing capacity of the subsoil and the load on the foundations. The greater the bearing capacity of the subsoil the less the width of the foundation for the same load.
Strip foundations on subsoils with poor bearing capacity, such as soft sandy clays, may need to be considerably wider than the wall they support to spread the load to a sufficient area of subsoil for stability.
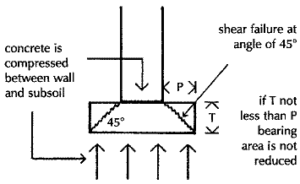
The concrete strip could be as thick as the projection of the strip each side of the wall which would result in concrete of considerable uneconomic thickness to avoid the danger of failure by shear.
The reason for the use of reinforcement of steel in concrete is that concrete is strong in compression but weak in tension. The effect of the downward pressure of the wall above and the supporting pressure of the soil below is to make the concrete strip bend upwards at the edges, creating tensile stress in the bottom and compressive stress under the wall. These opposing pressures will tend to cause the shear cracking illustrated in diagram below. It is to reinforce and strengthen concrete in tension that steel reinforcing bars are cast in the lower edge because steel is strong in tension. There has to be a sufficient cover of concrete below the steel reinforcing rods to protect them from rusting and losing strength.
Type of soil - Soft subsoil and poor bearing capacity. CLAY
Type of building structure - Masonry structure, like single terrace house.
Ref:
http://civilconstructiontips.blogspot.my/2011/06/foundation-construction-strip.html
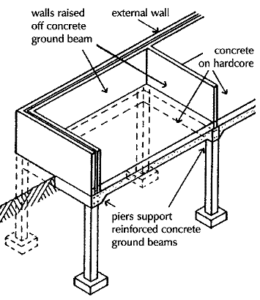
ii. Pad foundation
On made up ground and ground with poor bearing capacity where a firm, natural bed of, for example, gravel or sand is some few metres below the surface, it may be economic to excavate for isolated piers of brick or concrete to support the load of buildings of some four storeys in height. The piers will be built at the angles, intersection of walls and under the more heavily loaded wall such as that between windows up the height of the building.
Pits are excavated down to the necessary level, the sides of the excavation temporarily supported and isolated pads of concrete are cast in the bottom of the pits. Brick piers or reinforced concrete piers are built or cast on the pad foundations up to the underside of the reinforced concrete beams that support walls as illustrated in figure above. The ground beams or foundation beams may be just below or at ground level, the walls being raised off the beams.
The advantage of this system of foundation is that pockets of tipped stone or brick and concrete rubble that would obstruct bored piling may be removed as the pits are excavated and that the nature of the subsoil may be examined as the pits are dug to select a level of sound subsoil. This advantage may well be justification for this labour intensive and costly form of construction.
Type of soil - ground with poor bearing capacity where a firm, natural bed of, for example, gravel or sand is some few metres below the surface. CLAY & CHALK
Type of building structure - Masonry structure, like a 4 storey-shoplot.
Ref:
http://civilconstructiontips.blogspot.my/2011/06/pad-foundations.html
iii. Raft foundation
A raft foundation consists of a raft of reinforced concrete under the whole of a building. This type of foundation is described as a raft in the sense that the concrete raft is cast on the surface of the ground which supports it, as water does a raft, and the foundation is not fixed by foundations carried down into the subsoil.
Raft foundations may be used for buildings on compressible ground such as very soft clay, alluvial deposits and compressible fill material where strip, pad or pile foundations would not provide a stable foundation without excessive excavation. The reinforced concrete raft is designed to transmit the whole load of the building from the raft to the ground where the small spread loads will cause little if any appreciable settlement.
The two types of raft foundation commonly used are the flat raft and the wide toe raft.
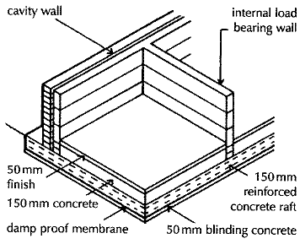
The flat slab raft is of uniform thickness under the whole of the building and reinforced to spread the loads from the walls uniformly over the under surface to the ground. This type of raft may be used under small buildings such as bungalows and two storey houses where the comparatively small loads on foundations can be spread safely and economically under the rafts.
The concrete raft is reinforced top and bottom against both upward and downward bending. Vegetable top soil is removed and a blinding layer of concrete 50 mm thick is spread and levelled to provide a base on which to cast the concrete raft. A waterproof membrane is laid, on the dry concrete blinding, against moisture rising into the raft. The top and bottom reinforcement is supported and spaced preparatory to placing the concrete which is spread, consolidated and finished level.
When the reinforced concrete raft has dried and developed sufficient strength the walls are raised as illustrated in diagram below. The concrete raft is usually at least 150 mm thick.
The concrete raft may be at ground level or finished just below the surface for appearance sake. Where floor finishes are to be laid on the raft a 50 mm thick layer of concrete is spread over the raft, between the walls, to raise the level and provide a level, smooth finish for floor coverings. As an alternative a raised floor may be constructed on top of the raft to raise the floor above ground.
A flat slab recommended for building in areas subject to mining subsidence is similar to the flat slab, but cast on a bed of fine granular material 150 mm thick so that the raft is not keyed to the ground and is therefore unaffected by horizontal ground strains.
Where the ground has poor compressibility and the loads on the foundations would require a thick, uneconomic flat slab, it is usual to cast the raft as a wide toe raft foundation. The raft is cast with a reinforced concrete, stiffening edge beam from which a reinforced concrete toe extends as a base for the external leaf of a cavity wall as shown in Fig. 13. The slab is thickened under internal load bearing walls.
Vegetable top soil is removed and the exposed surface is cut away to roughly form the profile of the underside of the slab. As necessary 100 mm of hardcore or concrete is spread under the area of the raft and a 50 mm layer of blinding concrete is spread, shaped and levelled as a base for the raft and toes. A waterproof membrane is laid on the dried concrete blinding and the steel reinforcement fixed in position and supported preparatory to placing, compacting and levelling the concrete raft.
The external cavity and internal solid walls are raised off the concrete raft once it has developed sufficient strength. The extended toe of the edge beam is shaped so that the external brick outer leaf of the cavity wall is finished below ground for appearance sake. A floor finish is laid on 50 mm concrete finish or a raised floor constructed.
Type of soil - compressible ground such as very soft clay, alluvial deposits and compressible fill material. PEAT & FILL
Type of building structure - Masonry structure, big building, complex.
Ref:
http://civilconstructiontips.blogspot.my/2011/06/raft-foundation.html