Q.
(a) With the aid of labeled diagrams explain the following roof structure for large single-storey factory building:
i) Lattice roof structure.
ii) Portal frame roof structure. (15 marks)
(b) Discuss the functional requirements of the roof for a single-storey factory building. (10 marks)
(25 marks, 2015 Q5)
A.
Similar question was asked in 2012 Q6 here.
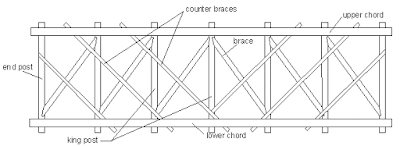
(a) (i) Lattice Roof Structure
Long-span industrial buildings can be designed with lattice trusses, using channel, beam or tubular sections. Lattice trusses tend to be beam and column structures and are rarely used in portal frames. Various configurations of lattice trusses are illustrated. The two generic forms are W or N bracing arrangements. In this case, stability is generally provided by bracing rather than rigid frame action.
Using lattice structures, a comparatively high stiffness and load bearing resistance can be achieved while minimising material use. Besides the ability to create long spans, lattice structures are attractive and enable simple service integration.
(ii) Portal Frame Roof Structure
The vast majority of single storey, steel framed buildings are portal frames. These were first widely used in the 1960s. During the 1970s and early 1980s they developed rapidly to become the predominant form of single storey construction. Using plastic design techniques first developed at Cambridge University, for spans up to about 50m portal frames are the most economical solution available. Large column-free areas can be achieved at relatively low cost. Often on multi-span frames the intermediate valley columns are omitted (‘hit-and-miss’) so that on, say, a 45m span frame, with bay centres of 8m, each column-free ‘box’ covers an area of over 700m2, which is nearly a fifth of an acre!
Portal frames typically use hot-rolled beams and columns for the roof rafters and supporting columns, although cold formed sections may be adequate for some small span structures. Portal frames come in a variety of different shapes and sizes, with flat and pitched roofs. The schematic arrangement of a typical single storey portal frame building is shown.
These simple types of structural systems can also be designed to be architecturally more appealing by using curved members, cellular or perforated beams etc. Innovative structural systems have also been developed in which portal frames are created by moment resisting connections using articulations and ties.
Ref:
http://www.steelconstruction.info/Single_storey_industrial_buildings#Types_of_portal_frame
http://www.steelconstruction.info/Single_storey_industrial_buildings#Lattice_structures
(b) functional requirements of the roof for a single-storey factory building
Similar question was asked in
D06 2012 Q3a
Function of roofing
ROOF GENERAL FUNCTION: To give a protective covering to the building, so rain, wind or snow may not damage the building .
4.The deflection of building may be cause of wind: occurrence of suction on the windward of slope of roof
Structural Stability
Provide a means of support for the roof covering. In designing a roof structure, the designer must take into consideration the span of structural members. If span at joist too great – bend To overcome : introducing a structural element which reduces the span
Provide Good Appearance
2.The detailing of roof can significantly affect the appearance of a building
Provide Thermal Insulation
4.Flat roof insulation is usually laid above the decking, either below or above the roof covering
ROOF COVERINGS
Is a materials which gives a protective surface to the roofing structure The function is only to prevent ingress or egress of heat & moisture into the building Various types of coverings depending on The character of the building The type of the roofing structure Local conditions, cost, etc.
Types of Roof Coverings
- Dead loads – roof structure, deck, insulation, roofing & any equipment located on top of or suspended from roof
- Live loads – accumulated rain, snow & ice & traffic if any.
- Wind loads – pressure or suction from wind
- Surface water from the outside
- Water vapor diffusion from the inside
- Moist air flow Heat flow & solar radiation
Madison O'Grady. Roofs. Slideplayer.com, available at